Global e-commerce sales rise to US$6.56–6.86 trillion in 2025 and exceed ~US$8.0–8.1 trillion by 2027-2028. The global market is expanding at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7–8%, which indicates consistent long-term growth. However, as mature markets stabilize, the pace may decrease. So, being a savvy and adaptable e-commerce business owner, you need to be one step ahead of your competitors. Therefore, maintaining a website alone is not enough to compete in this highly competitive industry. To improve your website’s ranking on search engines, you need to implement prominent search engine optimization (SEO) strategies. And there are various SEO techniques, like on-page, off-page, and local SEO, to dominate the local market. But the most important is technical SEO for an e-commerce site.
Every year, companies in the US spend more than $70 billion on SEO services. This figure has been rising consistently; it shows how important SEO has become to success online. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) simply means improving a website so it can pop up higher on Google, Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, or other search engines. The point is to help people find your site faster when they search online. The size of the SEO industry is huge, but that’s not the main factor. What is really important is knowing how to use e-commerce SEO the right way to get your website to the top of search results.
That’s why this blog gives you all the necessary details about technical SEO elements, like how to maintain site architecture and page speed and performance, and implement the right schema markup and all the basic navigation fixes to avoid duplicate content and so on. Go through the blog, and gradually you will discover all the necessary step-by-step guides of technical SEO for e-commerce optimization.
What Is Technical SEO for E-commerce and Why Does It Matter?
Before you delve into the technical considerations for an e-commerce site, you need to understand what technical SEO actually is.
The Foundation of Your Online Store Success
Technical SEO for e-commerce is the foundation of an online store. It focuses on optimizing the technical parts of your site—like speed, structure, and crawlability—so search engines can easily find, understand, and rank your pages.
An e-commerce site mainly revolves around two core page types: category pages and product pages. Both pages have their own significance to improve SEO strategy.
- Category Page
A category page helps customers to browse by type by grouping related products.
- Example: On an online clothing store, “Men’s Shoes” is a category page showing all types of shoes available (sneakers, boots, sandals).
- Product Page
A product page provides information about a single item that a buyer can purchase.
- Example: In the same store, “Nike Air Zoom Running Shoes” is a product page with a product description, price, size options, images, and reviews.
Goal- It makes sure that search engines understand the website structure, fixes technical SEO issues, and improves site speed and page performance
Key Elements of Technical SEO-
- Site Speed & Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-Friendliness
- Crawlability & Indexation
- Site Architecture & Site Structure
- Schema Markup
- Secure Website (HTTPS)
- Canonical Tags & Duplicate Content Fixes
- XML Sitemaps & Robots.txt
- Navigation & Internal Linking
- Fixing Errors (404s, Redirects, Broken Links)
Impact of Technical SEO for e-commerce
- Improves Recognition
- A site’s technical SEO helps search engines understand the content and layout of large e-commerce sites.
- It will improve crawlability, which will help e-commerce brands rank higher.
- Increases the User Experience
- Online shopping runs smoothly when pages have clear URLs and load effortlessly.
- Your website should have a responsive design for all devices, like mobile phones and tablets. The mobile-friendly design gets more potential customers.
- Supports Marketing Strategy
- The perfect, well-planned technical SEO is the backbone of every marketing strategy.
- It makes sure that the right keyword searches show up on product and category pages.
- Fixes Technical Issues
- Fixing duplicate content, broken links, and slow site speed raises credibility.
- This helps e-commerce brands attract customers and develop affection.
- Drives Conversions
- When search engines can easily index big e-commerce sites, it will automatically improve search rankings and organic traffic.
- More visibility means more traffic and sales from potential customers.
Top E-commerce Site That Correctly Optimized Technical SEO
As an example of good technical SEO for e-commerce site, here are 4 top e-commerce websites that SEO experts often recommend. None of them is “perfect,” but they are all good examples that you can learn from. I give each a name, a brief example, and the area in which they excel.
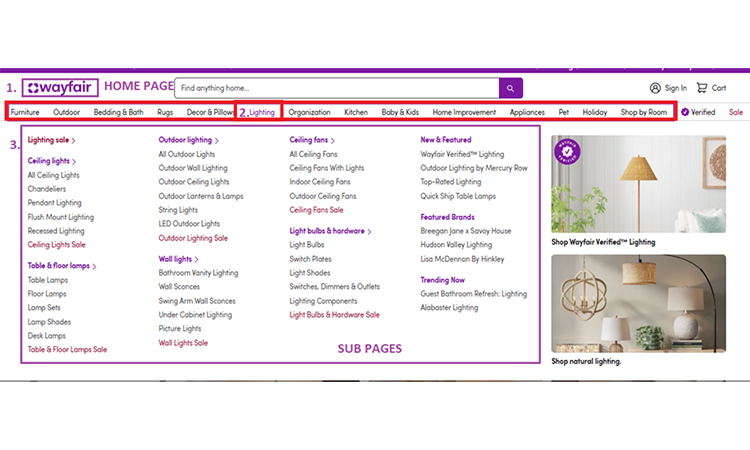
- Wayfair — Best: Faceted navigation & controlled crawlability
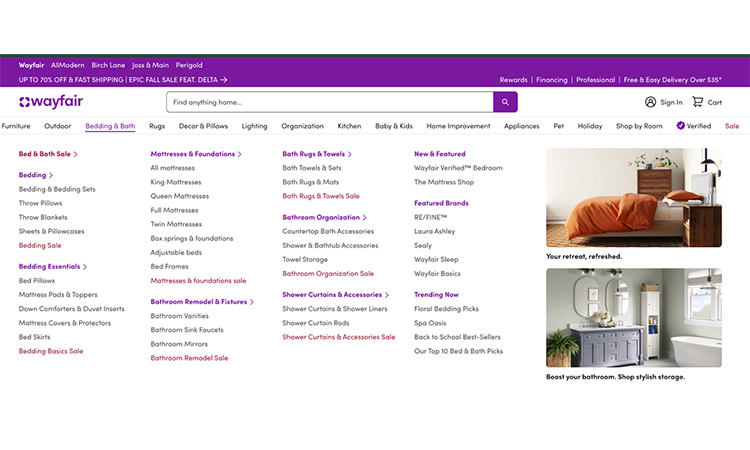
These e-commerce website has one of the best site structures. See, their category page is how professionally organized. A customer who has no idea of browsing can find any product of their choice. Each sections of their products are nicely optimized.
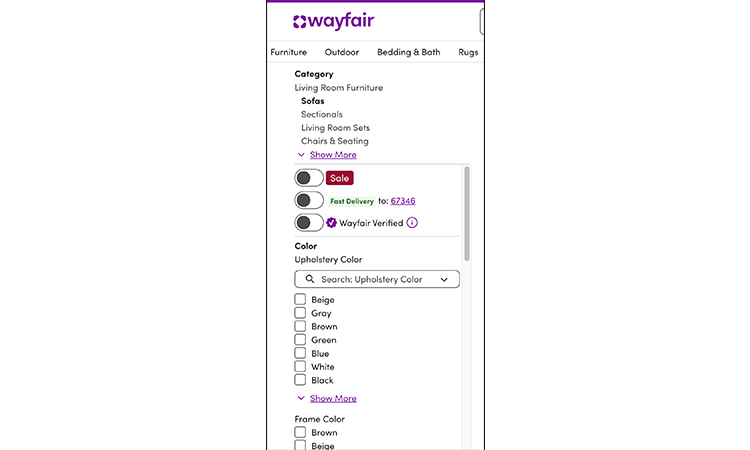
This website includes keywords in its main product headings. This helps clients to find it easily.
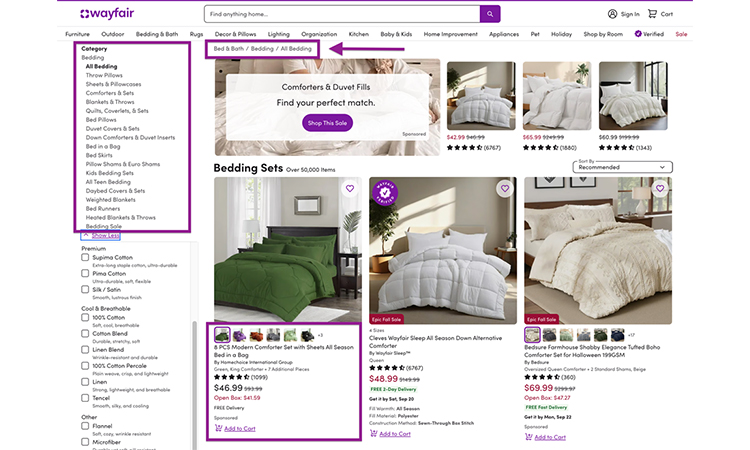
They provide a useful model for big e-commerce sites by keeping category pages crawlable while managing filter combinations.
- Etsy — Best: Structured data at scale (product/listing schema)
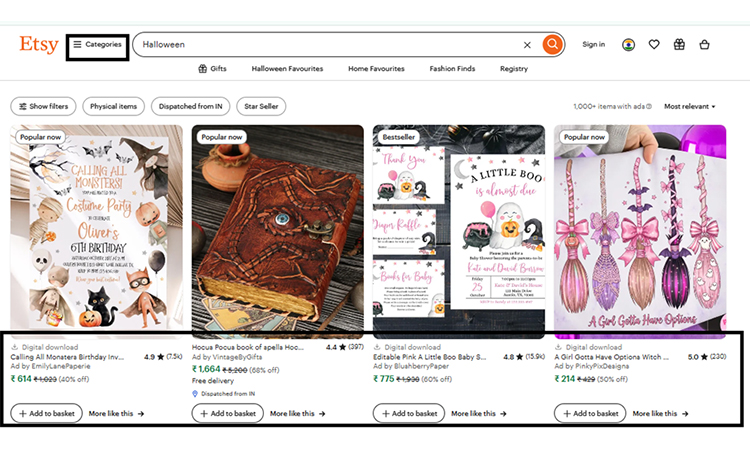
Etsy’s engineering team uses structured data across millions of listings to make their products more prominent to search engines.
Search engines can better comprehend thousands of distinct product pages by using Etsy’s implementation, which shows how a marketplace can scale schema (product, offers, and reviews).
- Walmart — Best: Large-scale site architecture, URL & schema hygiene
See how clearly its category sections are divided. If you want your website to be ranked higher, you have to implement this clear site crawl function. The site structure should be well optimized like this. You will learn the steps to optimize site architecture in the next segment.
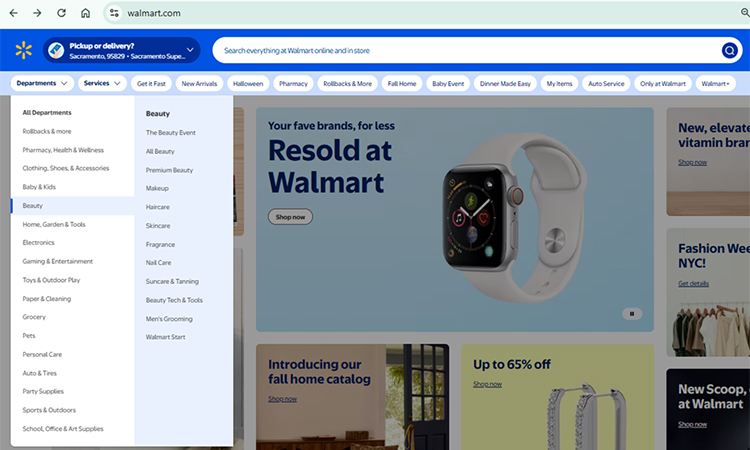
It took a lot of work and money for Walmart to make millions of SKUs easy to find by using technical SEO techniques like URL structure, schema, sitemaps, and overall meta hygiene. You can see how on-page and technical fixes at an enterprise level have helped Walmart in agency case studies and technical audits.
- Sephora—Best: UX-driven technical setup and page experience
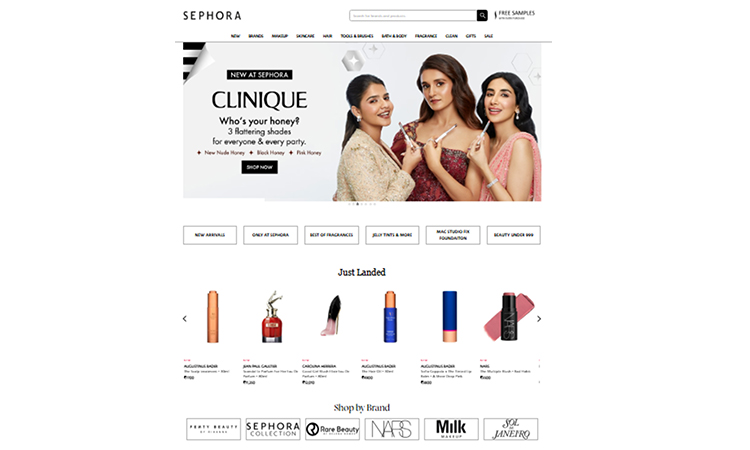
Online shoppers and experts agree that Sephora’s product and category UX, responsive/mobile experience, and emphasis on page experience make their product pages work well for both people and search engines.
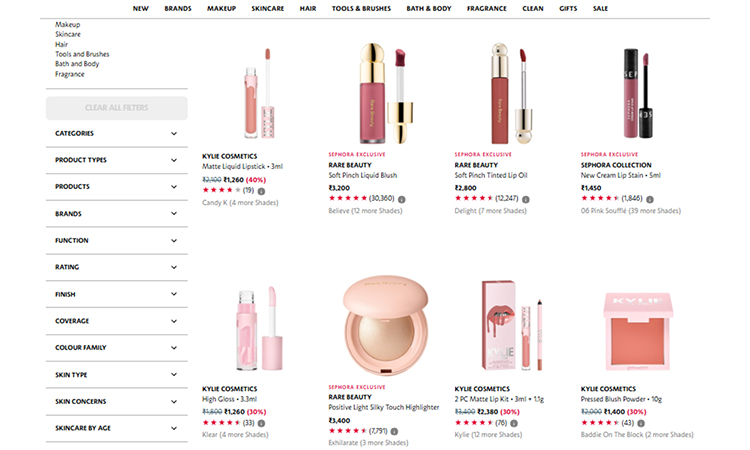
You need to improve the user experience of your e-commerce website, which links directly to SEO successes.
Quick Note: structured data and schema are a common strength across these sites because they help search engines provide rich results (reviews, prices, availability) — this is recommended by Google’s structured-data guidance. This can ultimately lead to higher click-through rates and increased organic traffic.
What are the Technical SEO Issues That Most E-commerce Sites Face?

- Duplicate Content Across Product and Category Pages-There is a lot of duplicate content on e-commerce sites. This is especially relevant when the same product is listed on more than one category page or when manufacturers’ descriptions are copied and pasted onto the site. This can hurt your search rankings because it gets search engine crawlers confused.
- Slow Site Speed and Poor Core Web Vitals-Page speed and Core Web Vitals are major challenges for large e-commerce sites. Heavy images, too many JavaScript files, or a lack of speed optimization can trigger slow load times. Slow-loading sites have higher bounce rates and fewer conversions.
- Broken Links and Crawl Errors-As product pages are updated or removed, broken links and reload chains often come up. These errors prevent search engines from crawling all the pages effectively, reducing the chances of valuable pages being indexed.
- Complex Site Architecture and Navigation Issues-Most of the e-commerce websites may have intricate site layouts with multiple layers of categories. Inadequate internal linking, orphan pages, or poor navigation make it hard for search engines and users to identify the most significant pages.
- Missing or Incorrect Schema Markup-E-commerce websites lose out on the opportunity to use schema markup to display rich snippets (such as prices or ratings) in the search results page, which can drastically reduce click-through rates.
Till now, you have learned about technical SEO for e-commerce and common technical issues e-commerce sites face, so in the next segment, you will learn the step-by-step process of technical implementations and all the solutions for technical e-commerce SEO issues. Stay tuned for more in-depth information on optimizing your e-commerce site for search engines.
How To Develop an E-commerce Site Architecture to Improve Online Visibility?
For both users and search engines, your website’s structure serves as a road map. Search engines require well-defined pathways to find and learn all of your content when they explore your e-commerce website. A well-organized site helps search engines connect your pages with what people are searching for.
- Develop A Search-Engine-Friendly Site Structure
Your website structure should be SEO friendly to generate rich results. This is one of the most significant parts of a technical SEO for e-commerce strategy.
- Logical hierarchy planning for maximum crawlability
- The 3-Level Rule: First, you can bookmark your most important pages within three clicks from your homepage. This means: Homepage → Category → Product/Article. The simple structure is best because search engines don’t crawl deeper pages as often.
- Pyramid Structure Works Best: Then you can start with your home page at the top. Below that, place your main category pages. Under each category, add subcategories if needed. Finally, place your individual product or content pages at the bottom.
Essential Steps:
- Make a list of all your pages and page types.
- Create a group of similar products.
- Make big groups (no more than 5-7). Organize the groups in a logical order based on user needs and preferences.
- Only add sections when you need to.
- All your pages should be linked to each other.
- Internal Linking Strategies for Product Discovery
There are bridges between the different parts of your website that are called internal links. They help search engines crawl multiple pages and figure out which pages contribute most.
- The Hub and Spoke Method: You can develop pillar pages for main topics. Then you may include related articles to these pillar pages. This indicates to search engines your areas of expertise.
- Contextual linking works best when you link to related goods or stories within your own material. If you’re writing about running shoes, connect to pieces that talk about running tips or shoe items that go with them.
Key Internal Linking Rules:
- Use descriptive anchor text (avoid “click here”).
- Link to 2-5 relevant internal pages per article
- Introduce new content to already popular pages.
- Review and update old content with new internal links.
- Page URL Structure Best Practices for E-Commerce
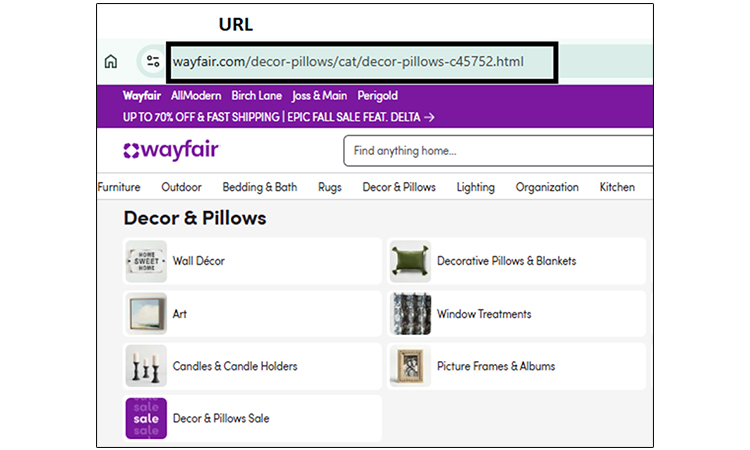
Your page URLs should explain the contents of each page to both search engines and users. So clean URLs should perform better in search results.
- Simple URL Formula: domain.com/category/subcategory/product-name
- Bad URL Example: yourstore.com/p?id=12345&cat=shoes&color=blue
- Good URL Example: yourstore.com/shoes/running-shoes/nike-air-max-2024
URL Best Practices:
- You need to implement hyphens instead of underscores.
- Then limit URLs to 60 characters when possible.
- Include target keywords naturally.
- Avoid special characters and numbers.
- Make URLs readable by humans.
- Category Organization and Taxonomy Planning
Smart category organization helps visitors find products faster and helps search engines understand your site’s structure.
The 7±2 Rule: People can easily process 5-9 options at once. Don’t overwhelm visitors with too many categories on one page.
Category Naming Strategy:
- You need to add those words that your customers actually search for.
- Avoid internal jargon or clever names.
- Keep category names short and clear.
- Test category names with real users.
Taxonomy Planning Steps:
- Research how competitors organize similar content.
- Analyze your search data for popular terms.
- Group products by customer intent, not just features.
- Create category descriptions for search engines.
- Plan for future growth and new products.
- Structuring Category Pages for Search Success
The main parts of your website are the category pages. They need a clear format so that search engines can understand what they’re writing and people can quickly find goods.
- Category Page Hierarchy and Organization
- Hierarchy Best Practices:
- Place category pages one level below your homepage.
- Use subcategories only when you have 10+ products per category.
- Assemble category names that match the search queries people use.
- Create category descriptions with target keywords.
- Organization Strategy:
- Group similar products logically.
- Use customer language, not technical terms.
- Plan for seasonal or trending categories.
- Include category images and descriptions.
- Pagination vs. Infinite Scroll Considerations
You need to decide how people will look through your many products when you have a lot of them. This choice changes how search engines crawl different pages.
- Pagination Benefits: Search engines can easily crawl all product pages. Users can bookmark specific pages. Better for desktop users who want quick navigation.
- Infinite Scroll Benefits: It will enhance the mobile experience to attract mobile traffic. Moreover, it will have higher engagement rates. And also, it reduces site load times initially.
SEO Implementation:
- For pagination: Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags.
- For infinite scroll: Implement SEO-friendly URLs for each section.
- Always provide sitemap entries for all products.
- Test crawlability with Google Search Console.
- Filter and Sorting Functionality Optimization
Smart filtering helps users find products faster without creating SEO problems.
- Filter Optimization Rules:
- Use canonical tags for filtered pages.
- Create SEO landing pages for popular filter combinations.
- Block unimportant filter combinations with robots.txt.
- Use structured data for product attributes.
- Sorting Best Practices:
- Default to the most relevant sorting for SEO.
- You can use certain page URL parameters that don’t create duplicate content.
- Include sorting options in your sitemap strategy.
- Monitor which sorting options users prefer most.
- Managing Duplicate Content Across Categories
Products often fit into multiple categories, creating duplicate content issues that confuse search engines.
- Solution Strategies:
- Choose one primary category per product.
- Use canonical tags pointing to the primary version.
- Create unique category descriptions.
- Add different related products to each category version.
- Search Intent Alignment for Category Pages
Different searches have different goals. Category pages must match what users actually want. You have to understand your users’ intent to improve SEO for e-commerce practices.
- Understanding Transactional vs. Informational Intent
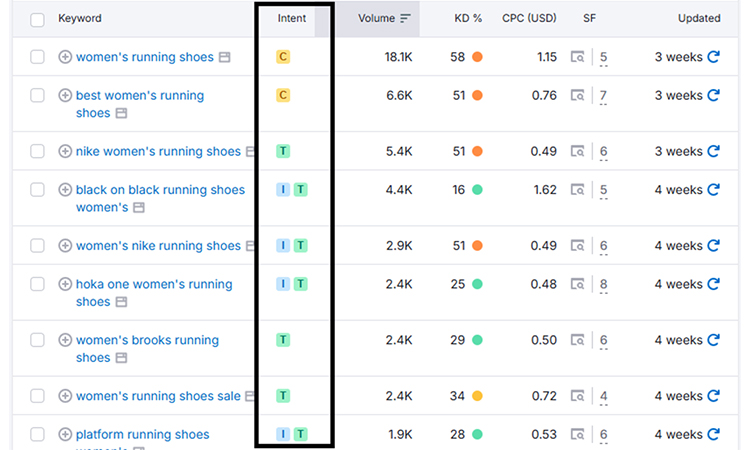
- Transactional Intent: Users ready to buy (e.g., “buy running shoes”)
- Focus on product listings and purchase options.
- Include price comparisons and reviews.
- Add clear call-to-action buttons.
- Optimize for “buy” and “purchase” keywords.
- Informational Intent: Users learning about products (e.g., “best running shoes for beginners”)
- Include buying guides and comparison charts.
- Add educational content and expert advice.
- Use FAQ sections and detailed descriptions.
- Target “best,” “how to choose,” and “guide” keywords.
- Keyword Targeting for Category-Level Searches
Category pages should target broader keywords than individual product pages.
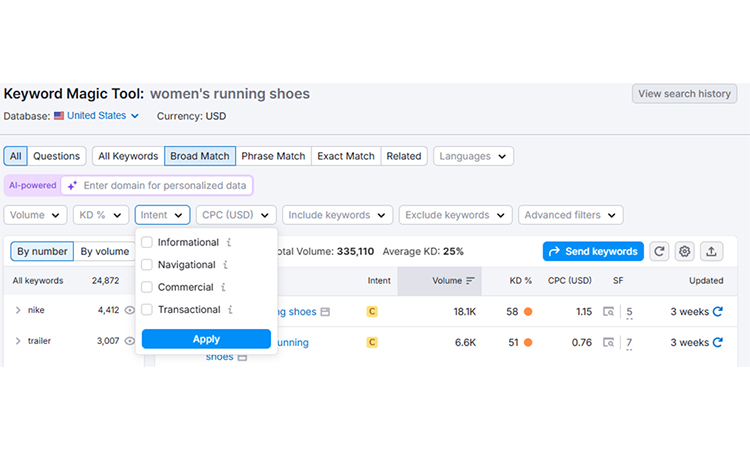
Keyword Strategy:
- Target category-level terms (e.g., “women’s running shoes”)
- Include brand and category combinations.
- Use location and category for local businesses.
- Research competitor category keywords.
You need to do keyword research for an e-commerce website to rank higher. So, you can take help from Google Keyword Planner, UberSuggest, and Semrush.
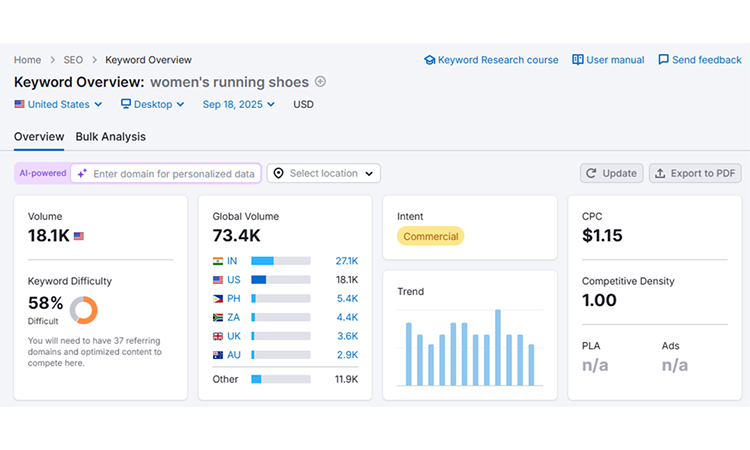
You can write your main keywords in the search bar of Semrush, and then you will see all the details and other relevant keywords.
Implementation Steps:
- Use primary keywords in page titles and H1 tags.
- Include related keywords in category descriptions.
- Add keywords naturally to product filtering options.
- Create a keyword-rich internal linking structure.
- Featured Snippets Optimization for Categories
Optimizing category pages can win featured snippets for comparison and list-type searches.
Optimization Techniques:
- Create “Best [Category] for [Use Case]” sections.
- Use numbered or bulleted lists for top products.
- Include comparison tables with clear headers.
- Answer common questions about the category.
How Core Web Vitals and Page Speed Impact Technical SEO for E-Commerce?
If your site loads slowly, it will directly affect your e-commerce business. Search engines use Core Web Vitals to figure out how to rank websites, which makes technical SEO for e-commerce more important than ever.
- Google Understands Page Experience Signals
Google uses something called “Core Web Vitals” to measure how users feel about the site. These indications help search engines find which e-commerce sites provide better user experiences.
The Three Core Metrics:
- Loading Performance: How fast your main content appears
- Interactivity: How quickly pages respond to user actions
- Visual Stability: How much content jumps around while loading
Why This Matters in SEO for E-commerce: Search engines give preference to websites that load quickly and function effectively. Your e-commerce brand is up against thousands of others in the same field. Technical SEO adjustments can increase sales conversions and rankings.
Real Impact on Business:
- 1-second delay = 7% conversion drop
- 3-second load time = 32% bounce rate increase
- Mobile users expect 2-second load times maximum.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) Optimization for Product Pages
LCP checks how long it takes for your biggest part to load. This is normally your major product picture or star ad on e-commerce sites.
LCP Target: Under 2.5 seconds for good performance
Common LCP Problems on Product Pages:
- Large, unoptimized product images
- Slow server response times
- Render-blocking CSS and JavaScript
- Poor hosting performance
Step-by-Step LCP Optimization:
- Optimize Hero Images:
- Compress images to under 100 KB when possible.
- Use WebP format for better compression.
- Set proper image dimensions in HTML.
- Preload critical images with <link rel=”preload”>.
- Improve Server Response:
- Choose hosting optimized for e-commerce.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN).
- Enable server-side caching.
- Optimize database queries for product data.
- Remove Render-Blocking Resources:
- Move non-critical CSS to load after the main content.
- Defer JavaScript that doesn’t affect initial rendering.
- Inline critical CSS for above-the-fold content
- Technical Implementation:

FID checks how long people have to wait for the page to reply after hitting something. INP (which will replace FID in 2024) tracks how fast a page is generally during a visit.
Target Metrics:
- FID: Under 100 milliseconds
- INP: Under 200 milliseconds
Common Issues on E-commerce Sites:
- Heavy JavaScript from tracking codes
- Complex product configurators
- Multiple third-party integrations
- Unoptimized event handlers
Optimization Strategies:
- JavaScript Optimization:
- Split code into smaller chunks.
- Load non-essential scripts after user interaction.
- Use web workers for heavy computations.
- Remove unused JavaScript libraries.
- Third-Party Script Management:
- Audit all tracking codes and plugins.
- Load scripts asynchronously when possible.
- Use Google Tag Manager efficiently.
- Delay non-critical third-party scripts.
- Event Handler Optimization:

- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) Prevention
CLS checks how much page information moves around while it’s loading. Users get annoyed when CLS scores are high, and it’s bad for technical SEO for e-commerce.
CLS Target: Under 0.1 for good performance
Common CLS Causes:
- Images are loading without being given a size
- Adding stuff dynamically
- Web fonts that change the style of text
- Places for advertisements
Prevention Strategies:
- Set Image and Video Dimensions:

- Reserve Space for Dynamic Content:
- Pre-allocate space for loading product reviews.
- Use skeleton screens while content loads.
- Set minimum heights for dynamic sections.
- Font Loading Optimization:
- Use font-display: swap for web fonts.
- Preload critical fonts.
- Include fallback fonts that match sizing.
- Advertisement Management:
- Reserve exact space for ad placements.
- Use static ad sizes when possible.
- Avoid inserting content above existing elements.
- Real-World Impact on E-Commerce Conversions
Your e-commerce business’s profitability is directly impacted by technical SEO enhancements.
Conversion Rate Improvements:
- 0.1-second improvement = 8% conversion increase
- Mobile speed optimization = 15% revenue boost
- Core Web Vitals compliance = 24% less abandonment
SEO for E-commerce Has Benefits for Large E-commerce Sites:
- Better crawling of indexed pages
- Improved link equity distribution
- Higher search engine rankings
- Increased organic traffic
- Image Compression and WebP Format Implementation
On e-commerce sites, images make up about 60 to 80% of the page weight. Smart compression makes speed much better.
WebP Benefits:
- 25-35% smaller than JPEG
- 25-50% smaller than PNG
- Supports transparency and animation
- Compatible with modern browsers
Implementation Steps:
- Convert Existing Images:

- Automated Conversion:
- ImageOptim and TinyPNG are good tools to use.
- Use conversion on the server side.
- Set up WebP to serve itself.
- For a flexible design, you should make images in a range of sizes.
- Advanced Optimization:
- Use progressive JPEG for large images.
- Implement the AVIF format for cutting-edge compression.
- Set up responsive images with srcset.
- Use lazy loading for below-fold images.
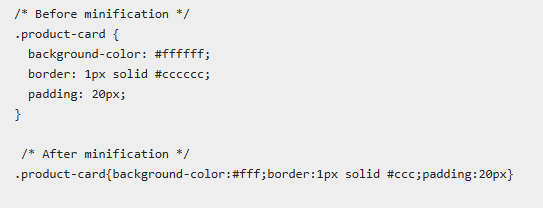
- CSS and JavaScript Minification Strategies
Moreover, you need to remove unnecessary characters from code files. It will reduce download times and improve technical SEO for e-commerce.
Minification Benefits:
- 20-40% file size reduction
- Faster parsing by browsers
- Reduced bandwidth usage
- Better mobile performance
Implementation Process:
- CSS Minification:
- Remove comments and whitespace.
- Combine multiple CSS files.
- Use CSS preprocessors with minification.
- Eliminate unused CSS rules.
- JavaScript Minification:
- Use tools like UglifyJS or Terser.
- Remove console.log statements.
- Shorten variable names.
- Eliminate dead code.
- Advanced Techniques:
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Setup
CDNs serve your content from servers closest to users, dramatically improving load times for your e-commerce website.
CDN Benefits:
- 40-60% faster load times globally
- Reduced server load
- Better handling of traffic spikes
- Improved SEO for international markets
Setup Steps:
- Choose the Right CDN:
- Evaluate global server locations.
- Compare pricing for e-commerce needs.
- Check integration with your platform.
- Consider features like image optimization.
- Configuration Process:
- Point static assets to CDN URLs.
- Set up proper caching headers.
- Configure SSL certificates.
- Test performance from different locations
- Optimization Strategies:
- Enable Brotli compression.
- Set long cache times for static assets.
- Use CDN for product images and videos.
- Implement edge-side includes for dynamic content.
- Lazy Loading for Non-Critical Resources
Lazy loading refers to the practice of postponing the loading of non-essential resources, such as scripts, images, or videos. They only load when the user moves to them. This makes the page load faster and gives users a better experience.
What to Lazy Load:
- Product images below the fold
- Customer reviews and testimonials
- Related product recommendations
- Social media embeds
Implementation Methods:
- Native Lazy Loading:
- JavaScript Libraries:
- Use Intersection Observer API
- Implement progressive image loading
- Add loading placeholders
- Handle fallbacks for older browsers
- Advanced Strategies:
- Lazy load entire product sections
- Defer third-party widgets
- Use virtual scrolling for long product lists
- Implement predictive loading for likely interactions
How To Implement Schema Markup for E-commerce SEO Success?
Search engine crawlers can better comprehend your content with the use of schema markup, which is distinct code. This structured data can significantly enhance the look and click-through rates of your search results for e-commerce SEO.
Essential Schema Types for Online Stores
Schema markup acts like a translator between your e-commerce website and search engines. It informs search engine crawlers exactly what each piece of content represents. It will help them display rich snippets in search results.
Why Schema Matters for E-commerce Businesses:
- It can increase click-through rates by 20–40%.
- Improves search results prominence with rich snippets
- Helps search engines understand product information
- Increases technical SEO for e-commerce sites
- Provides a competitive advantage on the search results page
- Product Schema Markup Implementation
The foundation of SEO for e-commerce is the product schema. It shows search engines about your products’ prices, availability, reviews, and specifications.
Essential Product Schema Properties:
- Name and description
- Price and currency
- Availability status
- Brand and manufacturer
- Product images
- SKU and model numbers
- Customer reviews and ratings
Step-by-Step Implementation:
- Basic Product Schema Structure:
- Advanced Product Properties:
- Add product alternatives for different sizes/colors.
- Provide shipping information.
- Specify warranty details
- Add energy ratings for appliances
- Include material composition
- Implementation Methods:
- JSON-LD (recommended): Add to page head
- Microdata: Embed within HTML elements
- RDFa: Use HTML attributes
Technical SEO Benefits:
- Price and availability can be shown by search tools.
- Items show up in Google Shopping results
- Click-through rates increase when search results are more accurate.
- Product details should be crawled and indexed better.
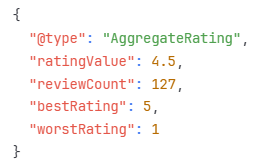
- Review and Rating Schema Setup
Review schema helps search engines display star ratings and review counts in search results, significantly improving click-through rates.
Review Schema Implementation:
- Individual Review Structure:

- Aggregate Rating Setup:
- Integration with Product Schema:
- Combine reviews with product markup.
- Include both individual and aggregate ratings.
- Update ratings dynamically as new reviews arrive.
- Ensure review authenticity and compliance.
Best Practices for Review Schema:
- Only include genuine customer reviews.
- Update aggregate ratings regularly.
- Include review dates and author information.
- Follow Google’s review snippet guidelines.
- Breadcrumb Schema for Navigation
Breadcrumb schema can show navigation paths in search results and enhance search engines’ comprehension of your site’s technical SEO structure.
Breadcrumb Schema Benefits:
- Displays the order of sites in search results
- Helps users understand how to navigate better
- It helps search engine bots figure out how a site is put together.
- Improves the look of mobile search results
Implementation Example:

Technical Implementation Tips:
- Match breadcrumb schema to visible navigation
- Use consistent URL structures
- Include all navigation levels
- Update dynamically for filtered pages
- Organization and Business Schema
Organization schema establishes your e-commerce business identity and provides essential business information to search engines.
Core Organization Properties:
- Business name and legal name
- Logo and contact information
- Physical address and phone
- Social media profiles
- Business hours and services
Complete Organization Schema:

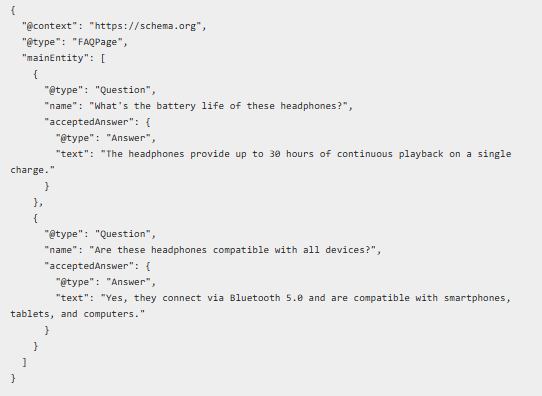
- FAQ Schema for Product Pages
FAQ schema can help your online store appear in featured snippets and voice search results. Moreover, it will drive additional traffic.
Strategic FAQ Implementation:
- Answer common product questions
- Address shipping and return concerns
- Explain product usage and compatibility
- Include troubleshooting information
FAQ Schema Structure:
- How-to Schema for Product Usage Guides
How-to schema helps your e-commerce business capture instructional searches and establish expertise.
Implementation Strategy:
- Create setup and installation guides
- Develop maintenance instructions
- Provide troubleshooting steps
- Include safety guidelines
How-to Schema Example:

- Video Schema for Product Demonstrations
Video schema is very significant for an e-commerce website. It will show relevant video thumbnails in regular search results.
Video Schema Properties:
- Video title and description
- Thumbnail URL
- Upload date and duration
- Video URL and embed URL
Implementation for Product Videos:
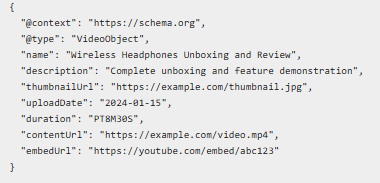
- Local Business Schema for Physical Stores
If your e-commerce business has physical locations, you need to implement the local business schema to improve local search visibility.
Local Business Schema Benefits:
- Appears in local search results
- Shows business hours and location
- Displays customer reviews and ratings
- Integrates with Google My Business
Complete Local Business Schema:

How To Optimize Navigation for Both Users and Search Engines?
In the process of technical SEO for e-commerce site, you have to fix navigation for users and search engines to show your website at the top. Here are some important components that you should implement to maintain a healthy e-commerce website.
What does “Navigation Fixes” mean?
In technical SEO for e-commerce, navigation fixes refer to improving how users and search engines move through your site.
It includes:
- Breadcrumbs → “Home > Category > Subcategory > Product” trails that improve UX and SEO.
- Menu Optimization → Clean, logical menus without too many layers.
- Internal Linking → Linking category pages to related products and vice versa.
- Faceted Navigation Fixes → Properly handling filters like color/size so they don’t create duplicate URLs.
- Pagination Fixes → Making sure multiple product listing pages don’t cause crawl issues.
In short: Navigation fixes = optimizing site architecture + site structure so shoppers and Google can easily find, crawl, and index all product and category pages.
Breadcrumb Implementation and Benefits
People can see where they are on your site and how they got there with breadcrumbs. They also help search engines figure out how your site is set up better.
- Breadcrumb Types:
- Location-based: Presents site hierarchy (Home > Shoes > Running Shoes)
- Attribute-based: Shows filters applied (Home > Shoes > Size 10 > Red)
- Path-based: Shows the user’s journey (rarely recommended)
- Implementation Benefits:
- Cuts down bounce rates by 20-30%
- Improves user experience on mobile devices
- Helps search engines crawl multiple pages quickly
- Provides additional keyword opportunities
- Technical Setup:
- Add structured data markup for breadcrumbs.
- Place breadcrumbs near the top of each page.
- Make breadcrumbs clickable links.
- Style them clearly, but don’t make them too prominent.
Mega Menu Optimization Techniques
The mega buttons can help you show a lot of access choices without making your design look cluttered. They improve user experience and help with e-commerce SEO when done correctly.
- Mega Menu SEO Benefits:
- Helps search engines discover more pages quickly
- Distributes link authority across important pages
- Reduces clicks needed to reach deep pages
- Improves internal linking structure
- Optimization Techniques:
- Include category descriptions with keywords.
- Add featured products or popular items.
- Use clear headings with target keywords.
- Keep load times fast with optimized images.
- Make menus work perfectly on mobile devices.
- Technical Considerations:
- Use HTML instead of JavaScript when possible.
- Add proper heading tags (H2, H3) in the menu structure.
- Include alt text for any images in menus.
- Test menu accessibility with screen readers.
Faceted Navigation Without Creating Duplicate Content
Faceted navigation helps users filter products by size, color, price, and other attributes. But it can make a lot of very similar pages, which makes search engines confused.
- The Duplicate Content Problem: If you have 100 products with 10 different filters, you could create 1,000+ similar pages. Search engines might not know which version to show in results.
- Smart Solutions:
- Use canonical tags to point to main category pages.
- Block filter combinations with robots.txt.
- Use JavaScript for some filters to avoid creating new URLs.
- Create landing pages for popular filter combinations only.
- Implementation Strategy:
- Identify your most popular filter combinations.
- Create SEO-optimized pages for these combinations.
- Use no-index tags for less important filter pages.
- Monitor crawl budget usage in Google Search Console.
Mobile Navigation Considerations
Mobile users behave differently from desktop users. Your e-commerce website structure must work perfectly on smartphones and tablets.
- Mobile-First Structure Rules:
- Prioritize thumb-friendly navigation.
- Keep main menu items to 5-7 maximum.
- Use large, easy-to-tap buttons.
- Implement search functionality prominently.
- Design for one-handed use
- Technical Mobile Optimization:
- Implement a responsive design that adapts to screen sizes.
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool regularly.
- Optimize page load speeds for mobile networks.
- Test navigation on actual mobile devices.
- Monitor mobile user behavior with analytics.
- Mobile Navigation Best Practices:
- Use hamburger menus wisely (don’t hide important links).
- Make search bars easily accessible.
- Implement voice search when relevant.
- Use swipe gestures for product galleries.
- Ensure the checkout process works smoothly on mobile.
Which Other Technical SEO Essentials Should E-Commerce Sites Focus On?
In technical SEO for e-commerce strategy, you need to check other factors like Crawlability And Indexation. Security flaws can negatively affect your e-commerce SEO performance. Search engines might show security alerts or remove hacked websites from their results. You have to regularly check your website’s security factors.
- Crawlability And Indexation Management
Beyond Core Web Vitals and schema markup, your e-commerce website needs additional technical SEO foundations to succeed. These essentials ensure search engines can properly crawl, index, and trust your online store.
- XML Sitemap Optimization for Large Catalogs
XML sitemaps make it easy for search engines to find their way around your e-commerce site. The sitemap must be strategically organized for large stockpiles to maximize the crawl budget. Your e-commerce website’s sitemap has to be added to Google Search Console. This allows for better indexation and visibility of your product pages.
Sitemap Structure for E-commerce SEO:
- Product Sitemap: Provide all active products with last modified dates.
- Category Sitemap: List all category and subcategory pages.
- Content Sitemap: Add blog posts, guides, and informative pages.
- Image Sitemap: Include product images for better prominence.
Implementation Best Practices:
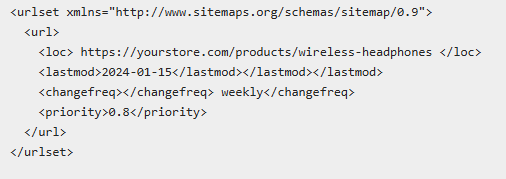
Advanced Strategies:
- Split large catalogs into multiple sitemaps (max 50,000 URLs each).
- Use sitemap index files for organization.
- Include only indexable, valuable pages.
- Update sitemaps automatically when inventory changes.
- Then you need to check the sitemap submission status in Google Search Console.
- Robots.txt Configuration for E-commerce
Robots.txt informs search engines which pages they can access, which helps you keep your e-commerce site’s crawl budget in check.
- Essential E-commerce Robots.txt Rules:
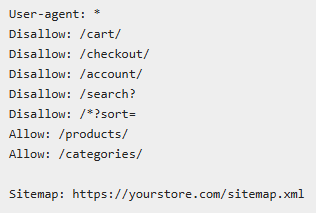
- Strategic Blocking:
- Block duplicate filtered pages.
- Prevent crawling of internal search results.
- Block user account and checkout pages.
- Set up important product and category pages.
- Block development and staging environments
- Technical SEO for E-commerce Benefits:
- Preserves crawl budget for important pages
- Prevents indexing of duplicate content
- Protects sensitive customer information
- Improves overall site crawling performance
- Canonical Tags for Product Variants
Product variants often create duplicate content issues. Canonical tags solve this by designating the primary version of each product.
- Common Variant Problems:
- Same product in multiple categories
- Different URLs for size/color variants
- Filtered and sorted product listings
- HTTP vs HTTPS versions
- Canonical Implementation:
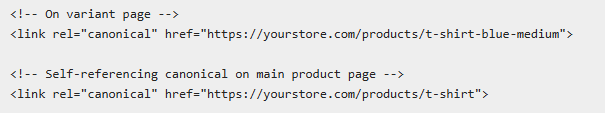
- Strategic Approaches:
- Canonicalize variants to the main product page.
- Use parameter handling in Search Console.
- Implement consistent canonical patterns.
- Monitor canonical tag effectiveness.
- Address canonical chain issues promptly.
- Managing Crawl Budget for Large Inventories
Large e-commerce sites must optimize how search engines spend their crawling resources to ensure all important pages get indexed.
- Crawl Budget Optimization:
- Prioritize high-converting product pages.
- Improve your e-commerce website speed to reduce crawl time per page.
- Fix crawl errors promptly.
- Remove or noindex low-value pages.
- Optimize internal linking structure.
- Monitoring and Improvement:
- Use Google Search Console crawl stats.
- Identify pages consuming excessive crawl budget.
- Improve server response times.
- Reduce redirect chains.
- Fix broken internal links.
- SSL Certificate Setup and HTTPS Migration
HTTPS is mandatory for e-commerce sites handling customer data. It’s also a confirmed ranking factor for technical SEO.
- Migration Steps:
- Purchase SSL Certificate: You can select an appropriate certificate type.
- Install Certificate: Configure on the web server
- Update Internal Links: Change all HTTP links to HTTPS.
- Set Up Redirects: Implement 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS.
- Update External References: Change links in social media and directories.
- Post-Migration Checklist:
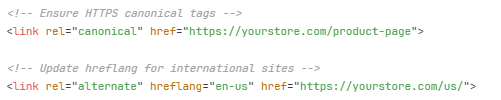
- Technical Considerations:
- Update sitemaps with HTTPS URLs
- Monitor for mixed content warnings
- Verify certificate chain validity
- Set up HSTS headers for enhanced security
- Update Google Analytics and Search Console properties
- Structured Data for Trust Badges
Trust signals in structured data help search engines understand your credibility and can display trust information in search results.
- Trust Signal Schema:

- Implementation Areas:
- Security certifications and badges
- Industry awards and recognitions
- Payment security indicators
- Customer service certifications
- Return policy guarantees
- Site Security Monitoring and Maintenance
You need to monitor your e-commerce site’s security. This is very important for technical SEO for an e-commerce site.
- Monitoring Activities:
- Regular security scans for vulnerabilities
- SSL certificate expiration tracking
- Malware and blacklist monitoring
- Payment system security audits
- Customer data protection compliance
- Maintenance Tasks:
- Update content management systems and plugins regularly
- Monitor for unusual traffic patterns
- Backup site data consistently
- Test security headers functionality
- Review user access permissions
Final Words Before We Conclude
Yes, technical SEO for e-commerce is very important to rank higher, but you don’t forget about other SEO strategies, including meta descriptions and meta titles. Your e-commerce website will rank higher and get more clicks when you optimize your on-page SEO for e-commerce and off-page with up-to-date content.
Maintaining technical SEO for e-commerce is a little bit strategic than other SEO strategies, so you can take an expert’s help. You can consult with one of the best e-commerce SEO agency to plan your technical SEO for e-commerce. But you have to take extra care for technical SEO optimization as it is the bae of your e-commerce website.
Additional Resources:
- The Beginner’s Guide to eCommerce Analytics
- SEO For Fashion E-commerce: Boost Your Sales Online
- How to Boost eCommerce Sales with Generative AI?

