A recent study reveals that 36% of respondents have used visual search, matching the usage rate of voice search.
In this digital era, are you struggling to find the real source of shared images? Then this Google reverse image search tool can help you out. You can discover the real source of your image and verify the authenticity of viral content or find visually similar images for your project.
Google’s reverse image search engine creates a revolution in visual content online. With the help of Google Lens, you can verify the image and get the real source and a similar picture. You don’t need keywords to search; simply upload the image and let Google do the rest. The search results will display websites where the image appears, as well as other sizes of the same image.
So. In this blog, you’ll get to know all the techniques of how you can use the reverse search bar and do fact-checking on the internet and how you use Google reverse image search on a desktop and phone, and so on. Let’s delve deeper into the world of the reverse photo search bar and resolve all queries for image file searches on Google.
What is Google Reverse Image Search?
Google’s reverse image search feature was first released in 2011. It uses advanced computer vision algorithms to deliver results. Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning grow their algorithms to make them better for finding pictures, matching images, and doing accurate visual searches. Today, it powers tools such as Google Lens, which present more innovative capabilities.
Google Reverse Image Search is a powerful visual search tool that helps you find related pictures and their source. It can be used to track down the original creator of an image or to verify the authenticity of a photo. You just need to paste the image URL or drag the image into Google Lens and let the tool do the rest. Reverse image search can reveal any copyright infringements associated with an image.
For example, you can take a photo of a plant and use Google Lens to search for information about it. Google Lens can translate text from images into different languages.
Difference Between Regular Search and Reverse Image Search
| Feature | Regular Search | Reverse Image Search |
| Input | Text-based keywords | Image file or image URL |
| Output | Text results (webpages, news, etc.) | Visually similar images, related pages |
| Use Case | General information lookup | Image source tracking, find similar images |
| Ideal For | Research, shopping, information | Fact-checking, copyright, image matching |
Why Should You Use Google Reverse Image Search?
There are various images surfing on the internet. But you don’t know which one is real or not. So you need to verify those images on Google Lens to know the actual source. These days, not everything you see online is real. People can take pictures, change them, or use them in the wrong way. With Google Reverse Image Search, you can look into things online like a detective. You can check facts, find sources, and be sure that the information you share is correct.
- Find the Original Source—You can identify the first appearance of the image on the internet. This gets you to the picture’s original creator, website, or photographer.
- Get Better Quality Images—There are times when you can find the same picture in a higher resolution or a different format. This is great for projects or presentations where you need a better copy.
- Verify If Something Is Real—Moreover, you can see if the image has been used in false news stories or if it’s been edited.
- Protect Your Own Work—You can see if someone is using your pictures without your permission if you are a photographer or online content creator. This supports your creative work and copyright. You can take legal action if necessary to protect your work.
- Shop and Learn About Products—Suppose you have seen a cool piece of gear or clothes in a picture? You can use reverse picture search to find a store that sells the item or find out more about it.
- Research Made Easy—You can also use reverse image search to learn more about any visual content you find online, whether you’re a student, a reporter, or just interested.
How to Use Google Lens for Reverse Image Search?
Google Lens is an advanced visual search tool that helps you search the web with pictures instead of words. You can use it to find visually similar images, scan documents, translate text, and more. It can recognize objects, text, places, and even products in real time.
Google Lens does more than 12 billion searches for images every month—Google I/O 2024
Installation and Setup
Android:
- On most devices, it’s already there.
- Get it from the Google Play Store if it’s not built in.
iOS:
- Take the Google app from the App Store and get it.
- This app has Google Lens built in.
Chrome Desktop:
- If you right-click on any picture in Google Chrome and choose “Search image with Google Lens,” you can use this function.
Step-by-Step Usage Guide of Google Lens
On Android/iOS:
- Open the Google app (or Google Lens app on Android).
- Press the camera-shaped Google Lens icon.
- Give access to the camera if asked.
- If you want to upload a picture from your device, point your camera at the object or tap the gallery icon.
- Lens will look through and show you matching images and relevant websites where you can find them.
On Desktop (Chrome):
- Right-click any image on a webpage.
- Select “Search image with Google Lens.”
- When you search for an image, the results show up in a side panel along with similar images and content.
How to Do a Reverse Photo Search on a Desktop (Step-by-Step)
You can easily do a reverse image search on your computer by using the Chrome browser or the Google Images site. Here are three easy steps that help you find the appropriate source of your image.
Method 1: Using the Google Images Website
If you already have an image file or a direct image URL, this is the best way to move it.
Step-by-Step Guide:
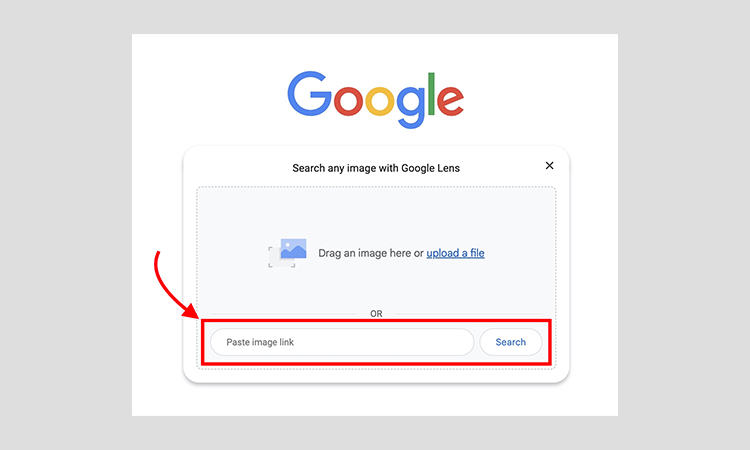
- First, you need to go to images.google.com in your browser.
- Then, you can press the camera icon in the search bar.
- Choose to either:
- Upload an image from your computer.
- Paste an image URL.
- When you click “Search,” Google will do an analysis and show you:
- It will find related images
- Moreover, it will display the same photo on other websites
- Relevant content
Method 2: Right-Click Method in Chrome
- After that, open Google Chrome and go to the page where the picture is.
- Then you can right-click on the picture and then—
- Select “Search image with Google Lens.”
- There will be a panel that shows:
- Images that match
- Results of the product (if any)
- It shows related images on other web pages.
Browser Compatibility:
- This process only works on Chrome (latest version).
- On Firefox or Safari, you’ll need to use Method 1 instead.
Method 3: Drag and Drop Method
Then explore images.google.com in one browser tab.
- After that, drag an image file from your computer or another tab.
- Drop it directly into the search bar.
- Google will do an image search in reverse automatically.
Browser Requirements:
- This method of image search is perfectly compatible with Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Opera.
- However, you need to ensure that you’ve enabled the browser’s drag-and-drop setting.
What File Formats Work with Google Reverse Image Search?
- Google Reverse Image Search accepts common image file formats, including JPEG, PNG, GIF, and WebP. These formats are commonly used, and Google’s reverse image search engine can identify them flawlessly. You can use any of these supported formats to upload an image or paste an image URL.
- However, to get the best results, you can upload images under 20 MB. But Google is not strict about the size, and this size is perfect for the drag-and-drop technique. It could take longer to analyze or even fail to upload files if your image is high resolution and size.
- Furthermore, to get precise results, use clear and good-quality images. But pictures should not be compressed too much. Always try to avoid heavily blurred or cropped visuals unless intentional. This can result in inaccurate or misleading data.
Best Practices:
- First, you need to decide whether the content and product photos will be JPEG or PNG.
- Then, you can use GIF only for single frames (not animations).
- WebP is supported, but older browsers don’t implement it as consistently.
- Always upload a high-resolution, uncropped copy of your photo for better matching images and picture results that look the same.
How to Use Google Reverse Image Search on Mobile?
Your phone or computer can both search with an image instead of text, so the basic function is the same. The methods and user experience are a little different depending on the device you’re using, though.
Google Reverse Image Search On Android Devices
- Using the Google App—Select the Google app and touch the camera icon next to the search bar. Then, you can pick “Search with your camera” and either take a new photo or grab one from your gallery. Google will immediately show you the results of a reverse image search.
- Chrome Browser Method—These techniques are the same as you do on desktop using method 2. You need to tap on the camera icon on your mobile device. Then upload your picture. You can also hold down on any picture on a website and choose “Search Google for this picture” from the menu that appears.
- Google Lens Integration—Google Lens is already there in various mobile devices. So you just upload a picture on Lens, or you can point your phone’s camera at the object you search for. Then Google images does its job, and your required information will be served.
Is the Image Search Method the Same on Apple (iPhone) and Android?
Apple (iOS) and Android devices both have the same basic features: you can reverse image search with Chrome, Google Lens, or the Google app. However, the two platforms are a little different in how they are accessed and how they are used.
Common Methods on Both Platforms:
- On both Android and iPhone, use the Google app with the Google Lens feature.
- If you want to identify a picture with Google Lens, then tap on it in Chrome and choose “Search image with Google Lens.”
- In desktop mode, go to images.google.com and upload or paste a picture URL.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Android | Apple (iOS) |
| Google Lens App | Often preinstalled | Not available as a standalone app |
| Google App with Lens | Full access | Available via the Google app |
| Chrome “Search Image” Option | Fully integrated | Works, but fewer Lens features |
| Uploading from Gallery | Direct access via Lens | Requires using the gallery through the Google app |
How Does Google Reverse Image Search Work?
Google reverse image search relies on advanced computer vision technology to evaluate and match images across the web. Here’s how this effective reverse image search engine works behind the scenes.
- Technical Explanation (Simplified)- Google Images and Google Lens on your phone and computer both turn your photo into digital fingerprints when you upload it. The colors, shapes, patterns, and objects in the picture are some of the important details that these fingerprints pick up.
- Image Recognition Algorithms—Machine learning algorithms are used by Google’s reverse search technology to figure out what’s in your picture. This algorithm can recognize faces, objects, landmarks, text, and even complex scenes. When you tap the camera icon in the search bar or click search, these algorithms start evaluating your uploaded image immediately.
- Visual Similarity Matching—Your photo is compared to billions of images in Google’s database by the reverse image search engine. It searches other websites for images that match and have a similar aesthetic. This system finds pictures that have similar visual elements, even if they are bigger or smaller or have been lightly manipulated.
- Database Comparison Process—Search engines crawl the whole web to gather pictures for their huge database. When you search by image, the system examines this database to find related images and discover the primary author. Moreover, you can see the online locations of your picture, along with similar images and websites that have the same photo.
This visual search technology works on any browser, from desktop computers to mobile phones. Anyone can use Google Lens to find similar images and identify objects with amazing accuracy, whether they drag and drop a file, paste an image URL, or use the camera on their phone.
How to Use Reverse Image Search for Fact-Checking and Copyright Protection?
You can use reverse image search to find the truth and keep your creativity safe online, not just because you’re interested.
Check If an Image Is Real or Fake
Many people share fake photos or edited images online to mislead other people. So, you can use Google Reverse Image Search to determine if an image is genuine. This is especially helpful for students, journalists, or anyone researching online.
- You can check which platform this picture first appeared on.
- Then, you can check if the same picture was used on other reputable news sites.
- After that, you should verify if the picture is used in the right way or the wrong way. Finally, you can use online tools to analyze the metadata of the image.
- This is very useful for checking pictures or jokes that are going viral.
Spot Fake or Changed Images
You can also find manipulated content, such as altered backgrounds or photoshopped faces, by using reverse image search. You can:
- You can also search for similar images.
- Then you need to compare them to the original to determine any discrepancies.
- You need to confirm with legitimate news or photo websites.
Protect Your Photos from Being Stolen
Reverse image search is useful for protecting your online work as a photographer, artist, or content creator.
- You need to search for similar websites that used your image file without permission.
- Then, you should identify unauthorized use of your content.
- After that, you can see if someone shared your same photo or an edited version of your picture.
What Can You Do If Someone Steals Your Image?
If you think someone is using your picture without your permission, you can:
- Verify that it’s a legal use, like for school, news, or reviews.
- If it isn’t, send a DMCA takedown request to the website and ask them to take it down. Google had over 75 million DMCA takedown requests every month.
- Moreover, you can use tools like Pixsy or TinEye to record more prohibited uses.
- For better security, you can add a watermark to your pictures.
What Are The Best Alternatives To Google Reverse Image Search?
The following search engine has unique strengths, so using multiple platforms gives you the most complete results.
- TinEye – The Pioneer-TinEye was the first reverse image search engine and remains highly accurate for finding exact image matches. It’s excellent for copyright protection and tracking image usage across the web. TinEye searches over 76.5 billion images and shows when and where images first appeared online.
- Bing Visual Search Image—Microsoft’s Bing Visual Search offers strong results and integrates well with shopping searches. It’s particularly good at identifying products and landmarks and providing related visual content. The interface is user-friendly and works seamlessly across devices.
- Yandex Images—Russia’s Yandex Images excels at finding similar faces and objects. It often discovers results that Google misses, especially for European and Asian content. Yandex is particularly effective for finding people and social media profiles.
- Baidu Image Search Image—China’s Baidu Image Search dominates Asian markets and finds content from Chinese websites that other engines might miss. It’s essential for research involving Asian subjects or content.
How to Improve Your Reverse Image Search Results?
- Image Quality Optimization—You need to use high-quality images for better search results. The images should be clear; sharp photos work better than blurry or pixelated ones. You need to ensure that your image has good lighting and isn’t too dark or overexposed.
- Cropping and Editing Tips—Then, you should eradicate extra backgrounds or focus on the main subject. You can crop the image to only display the item you’re looking for. This helps the search engine concentrate on the most important issues.
- Multiple Search Engine Strategy: Moreover, don’t depend on just Google Images. So, you can try other reverse search engines like Bing Visual Search, TinEye, or Yandex Images. Every search engine has its database, so some may find results that other engines don’t.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- “No Results Found” Solutions—You can explore different renditions of your image. Rotate, resize, or adjust the brightness. Moreover, you can make a slight adjustment to make your image better recognized by the system.
- Slow Loading Problems—Further, you need to check your internet connection. Or else you can upload small-sized images.
- Mobile App Issues—You need to always update your Google app. Then you should clear the app cache if searches aren’t working properly on your phone.
- Browser Compatibility Problems—Furthermore, you may select Chrome or Safari for best results. Not all reverse search functions are supported by every browser.
Privacy and Security Considerations
- Data Collection and Storage—Google briefly saves shared pictures so that they can be processed. When you upload private or sensitive photos that you don’t want saved on their computers, be careful.
- Protecting Sensitive Images—You should share only those pictures that can be shared publicly. Otherwise, Google stores all pictures, so don’t ever share any sensitive or private images on public platforms. Additionally, consider using high-resolution images to improve the accuracy of your reverse image search results.
Future of Reverse Image Search Technology
- AI and Machine Learning Improvements—Artificial intelligence will create a paradigm shift in search-by-image techniques. One day, computers will be able to understand more than just the patterns in pictures. They will also be able to figure out what the pictures mean. AI will recognize heavily edited photos, deepfakes, and altered content more precisely.
- Integration with AR/VR—Augmented reality and virtual reality will change how we search for images. Soon, you’ll point your phone’s camera at any object and instantly get information about it. AR glasses will overlay search results directly onto what you’re looking at. You can search through image databases in virtual reality environments, and they help you navigate them in 3D. This makes research more interactive and real.
- Enhanced Mobile Capabilities- Mobile reverse image search will become faster and more accurate. Your phone’s camera will work like a super-powered search engine, discovering everything from creatures and animals to products and landmarks in real time. You can search for images offline, which means you can use databases stored on your device even when you’re not connected to the internet.
- Industry Predictions and Trends- Experts predict reverse image search will become part of everyday life. Shopping apps will let you photograph items to find where to buy them instantly. Social media platforms will use the technology to fight fake news and identify misleading images. Privacy-focused search engines will offer secure image searching without storing your data.
The future promises faster, smarter, and more private reverse image search tools that work flawlessly across all devices and platforms.
What Are The Limitations Of Google Reverse Image Search?
- Privacy Concerns and Restrictions- There are privacy concerns about sensitive content because Google temporarily stores uploaded images so that they can be processed. The service might not work right with VPNs or private browsing modes, which makes it harder to search anonymously.
- Regional Availability Issues- Most of the time, Google Reverse Image Search works everywhere. However, some countries have privacy laws, censorship, or national rules that make it hard to use Google services or image search tools.
- Countries with Restrictions on Reverse Image Search:
| Country | Restriction Type | Reason |
| China | Google is blocked entirely | Government censorship |
| North Korea | No access to Google or the internet | State-controlled internet |
| Iran | Google services are partially blocked | Political and social control |
| Turkmenistan | Heavily censored internet | Government control |
| Syria | Limited or filtered access to Google tools | Government-imposed restrictions |
- Database Coverage Gaps- Google can’t index every image on the internet. There are various private social media like Facebook profiles, password-protected sites, and recently uploaded content that may not appear in search results. They don’t fully cover all smaller websites and regional platforms.
FAQ Section
Google does not store your reverse image search history unless you’re logged in and have Web & App Activity turned on. Your Google account settings allow you to view or delete your activity at any time.
Google Reverse Image Search can find similar photos of people, but it’s not designed for facial recognition. It could help you find public profiles or pictures that have been used elsewhere, but it won’t directly identify people you don’t know.
Yes, Google Reverse Image Search is completely free to use on both mobile and desktop. You can upload images, paste URLs, or use Google Lens without any subscription or payment.
No, Google Reverse Image Search requires an internet connection. It runs your picture through web computers to see how it compares to billions of other pictures. Anyone can’t use it when they’re not online.
Go to your Google My Activity page, select “Web & App Activity,” and delete specific image searches. If you were not logged into a Google account, no history is saved to delete.
Let’s Conclude
Here, we are at the end of our conversion of Google Reverse Image Search. So after all these steps, you should now have a better understanding of how to use this tool effectively for finding similar images online. Remember to always double-check the results and verify the sources before reaching any conclusions based on the search results.
In this era of misleading people, Google Reverse Image Search can be a valuable tool in ensuring the authenticity of images circulating online. You can consider the above-mentioned steps and exercise caution; you can navigate the digital landscape more confidently and accurately discern the origins of images you come across.